Principle of Sapphire Laser Cutting
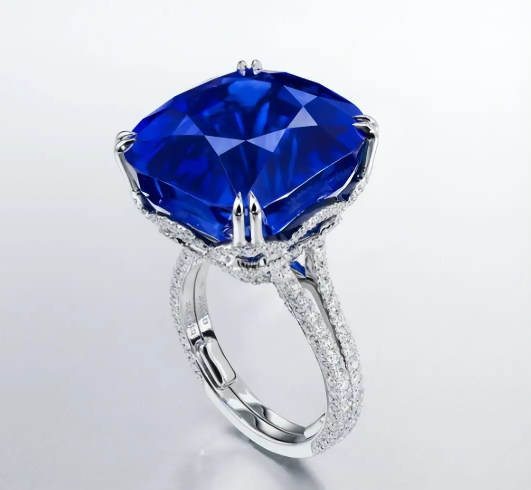

Laser sapphire cutting, particularly for applications such as LED chip substrates, watch lenses, and smartphone camera protective lenses, primarily relies on the core principle of "thermal spalling control cutting," also known as "laser-induced thermal spalling" or "invisible cutting.".
Core Principle: Laser-Induced Thermal Cracking
The key to this technology is focusing ultra-short pulse lasers (typically picosecond or femtosecond lasers) inside the sapphire crystal, triggering localized nonlinear absorption to generate an extremely small, controllable micro-cracked layer (modified layer) without damaging the material surface.
Main application areas
LED Industry: Used for cutting sapphire substrates (2-inch, 4-inch, 6-inch wafers), which is the earliest and most significant application of this technology. High yield and crack-free edges are crucial for the performance of LED chips.
2. Consumer Electronics: Cutting sapphire screens or components for devices such as smartphone camera lens protectors, Home button covers.
3. Watchmaking Industry: Cutting sapphire crystal lenses for high-end watches.
4. Industry and Optics: Cutting sapphire for window substrates, sensor protective lenses, and special optical components.
The principle of laser sapphire cutting essentially involves using ultrafast lasers to "draw" an invisible fragile plane inside the sapphire, which is then cleanly separated like breaking apart a biscuit. This method perfectly addresses the challenges of precision cutting for sapphire—a material with high hardness, brittleness, and melting point—achieving high-quality, high-efficiency, and highly flexible "cold processing," making it a key technology in modern precision manufacturing.